Introduction to Transactions in Ethereum
Last Updated on 8. August 2023 by Mario Oettler
The purpose of a transaction is to change the state of the Ethereum network. Suppose Alice owns 2 ETH. If she sends 1 ETH to Bob, this change is recorded in the transaction. And the state would change like in the following chart:
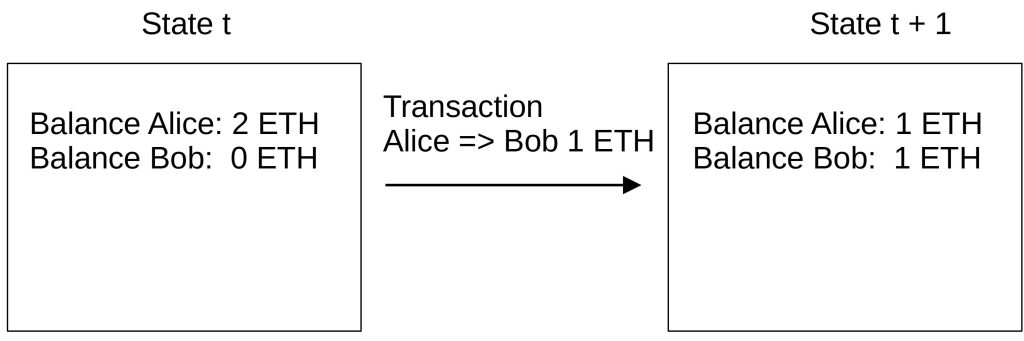
Unlike UTXO-based models like Bitcoin, in Ethereum, balances are assigned directly to an address.
Transactions need a signature that corresponds to the sender. Only if the signature is correct the transaction can be considered as valid.
There are three kinds of transactions:
- Normal value transfers. Transfers ETH to another EOA.
- Account creation: they don’t have a “to” address. The data field contains the contract code.
- Execution of smart contracts: The data field contains the function and the parameters. The “to” address is the address of the smart contract.

 Register
Register Sign in
Sign in