Present Value
Last Updated on 23. November 2023 by Mario Oettler
In this topic, we learn what the present value is and how it is calculated.
The general formula for calculating the present value is:
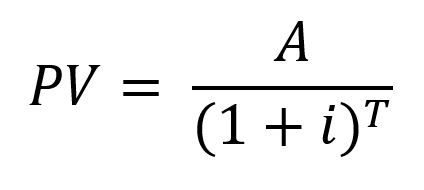
PV: Present value
A: amount of the future payment
i: interest rate
T: period of the future payment (or number of periods between payment and valuation period)
The present value tells us, how much a future payment (e. g. in period t2) is worth in the present (period t0).
Example of Present Value
In this example, we calculate the present value for the information given:
Interest rate i = 5%
Payment period T = 3
Amount A = 200 EUR
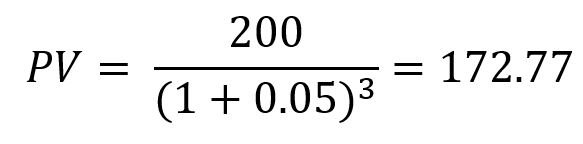
Interpretation of the Present Value
Since the present value tells us, how much a future payment is worth in the present, the interest rate can be interpreted as a time preference. The higher the interest rate, the more an individual values the present.
Looking at our example, if someone offered us more than 172.77 EUR in t0 on the condition that we waive the payment in t3, we would accept.
If we were offered less than 172.77 EUR in t0, we would wait for t3 and pocket the 200 EUR, because they would be worth more to us.
The present value is the equivalent of how much a current payment is worth in the future if it earns interest.
The present value of 172.77 EUR in our example would be worth 200 EUR in three periods (t3) at an interest rate of 5%.

 Register
Register Sign in
Sign in